Deploy a Django App on Leapcell
If the solution below does not resolve your issue, feel free to join our Leapcell Discord community for further assistance.
You can deploy a Django Python app on Leapcell in just a few clicks.
This quickstart uses a simple example app, but you’re welcome to use your own Django app instead.
You’ll need a GitHub account to proceed. If you don’t have one, you can create on the GitHub website.
1. Fork the Django example on GitHub.
Repo: Django example
This is a simplified Django program based on the Django Tutorial.
If you’re new to Django, we recommend following the Django Tutorial first.
2. Create a Service in the Leapcell Dashboard and connect your new repo.
Go to the Leapcell Dashboard and click the New Service button.
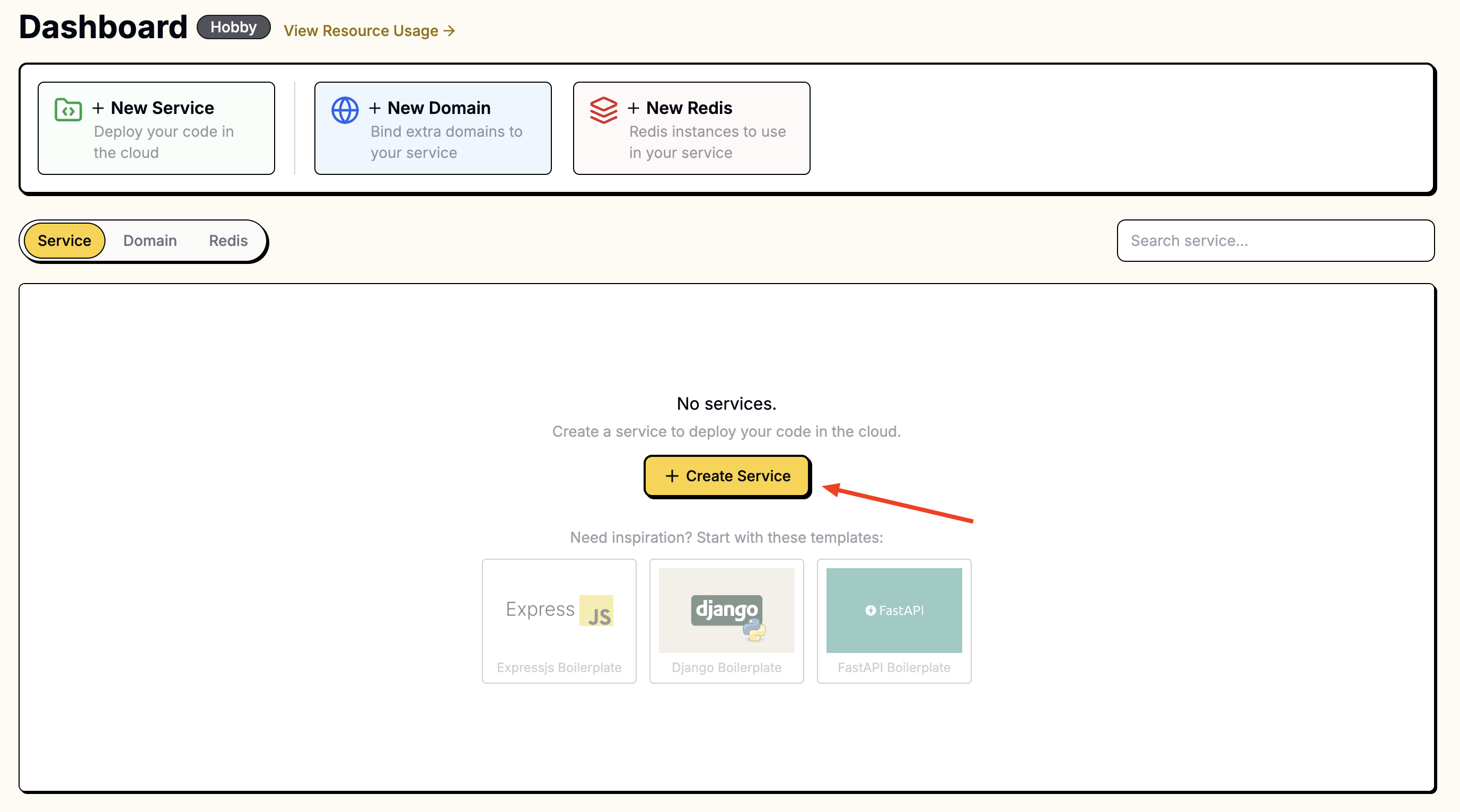
On the "New Service" page, select the repository you just forked.
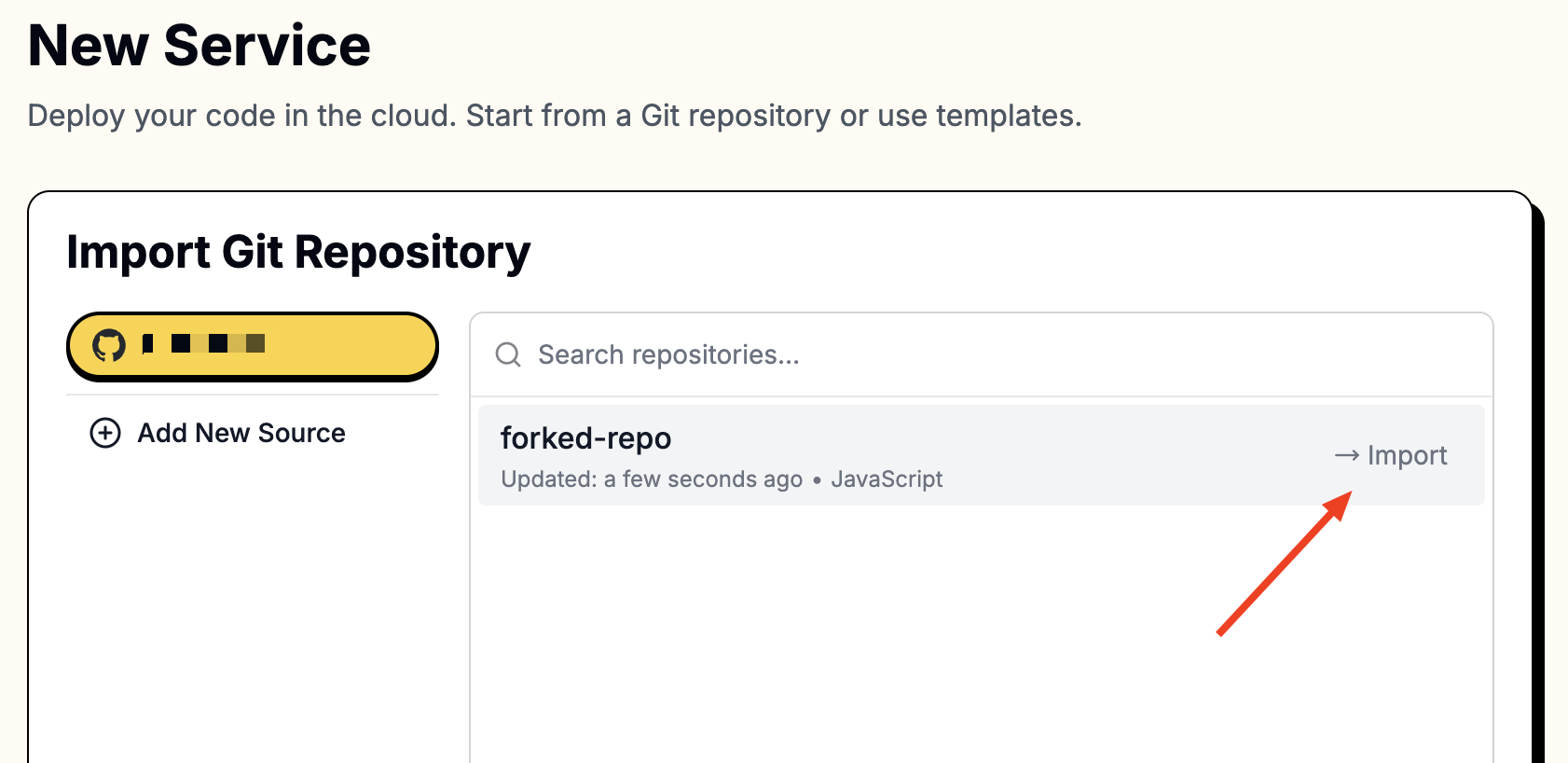
To access your repositories, you’ll need to connect Leapcell to your GitHub account.
Follow these instructions to connect to GitHub.
Once connected, your repositories will appear in the list.
3. Provide the following values during creation:
We will use Gunicorn to run the Django app, so ensure you add gunicorn to your requirements.txt.
Below are the basic configuration details for setting up a Django service on Leapcell:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Runtime | Python (Any version) |
| Build Command | pip install -r requirements.txt |
| Start Command | gunicorn myproject.wsgi --bind 0.0.0.0:8080 |
| Port | 8080 |
Enter these values in the corresponding fields.

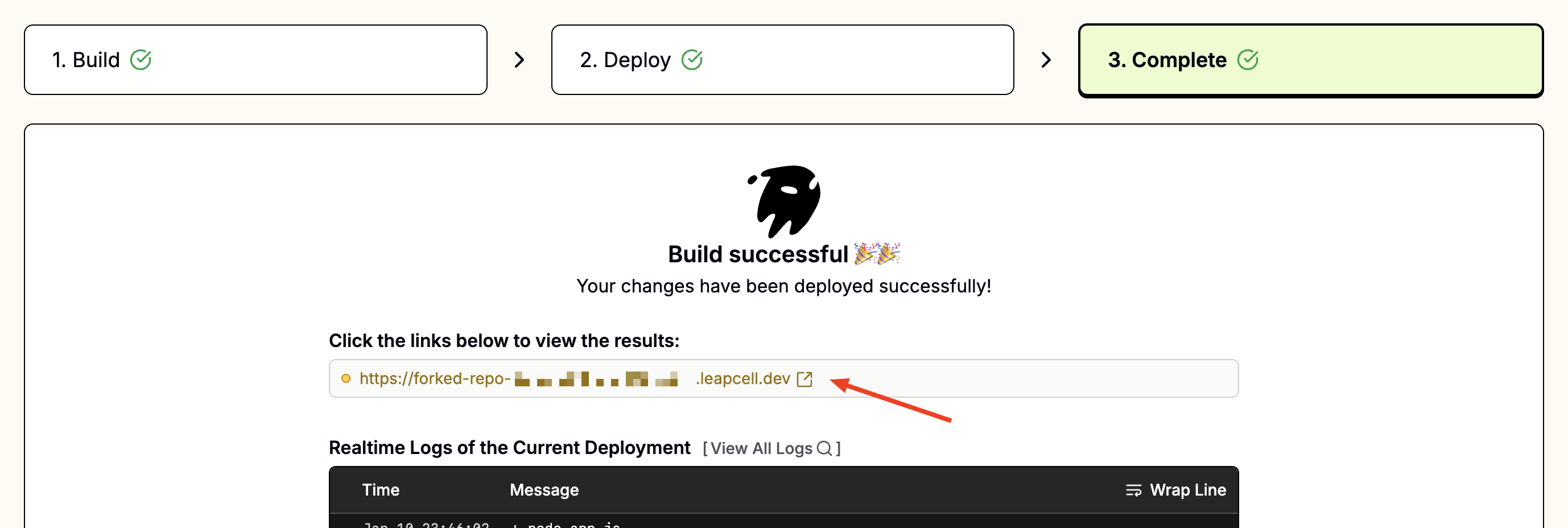
4. Access Your App:
Once deployed, you should see a URL like foo-bar.leapcell.dev on the Deployment page. Visit the domain shown on the service page.
Continuous Deployments
Every push to the linked branch automatically triggers a build and deploy. Failed builds are safely canceled, leaving the current version running until the next successful deploy.
Learn more about Continuous Deployments.