Serverless vs. Persistent Servers
Leapcell은 다양한 애플리케이션 요구 사항을 충족하기 위해 두 가지 주요 배포 모드인 **서버리스(사용한 만큼 지불)**와 **영구 서버(시간별 요금)**를 제공합니다.
Leapcell에서는 언제든지 서비스 모드를 서버리스와 영구 서버 모드 간에 전환할 수 있습니다. 특정 사용 사례에 가장 적합한 모드를 선택할 수 있습니다.
:::
이러한 고유한 기능과 장단점을 이해하면 프로젝트에 가장 적합한 옵션을 선택하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
서버리스(사용한 만큼 지불)
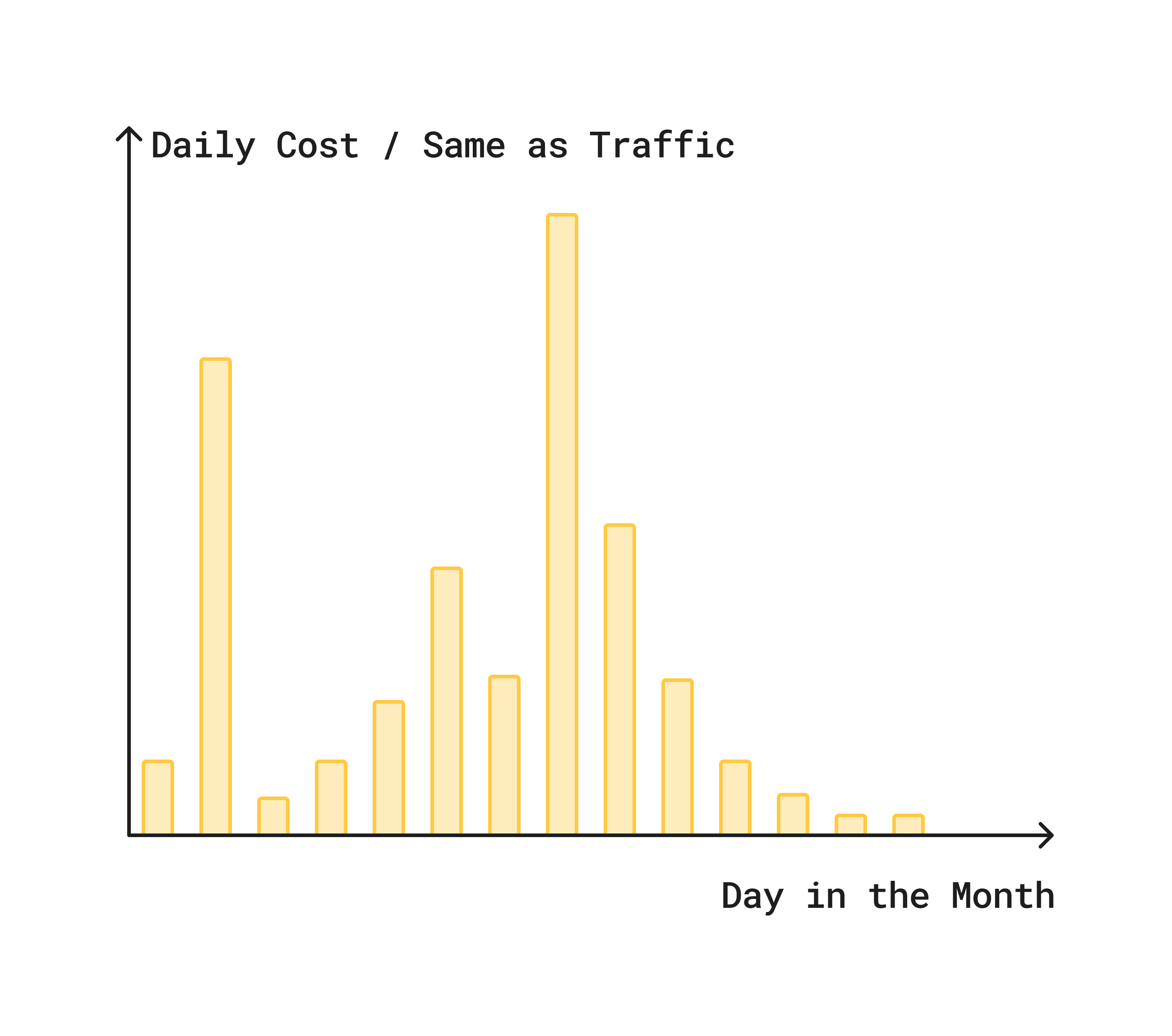
서버리스 모드는 코드 실행 시간**에 대해서만 요금을 지불하는 이벤트 기반 컴퓨팅 모델입니다.
요금은 요청이 수신되면 시작되어 요청이 완전히 처리되면 종료됩니다. 애플리케이션이 트래픽을 처리하지 않는 유휴 시간 동안에는 비용이 발생하지 않습니다.

자동 확장
이 플랫폼은 트래픽 볼륨에 따라 인스턴스 수를 자동으로 확장하거나 축소합니다.
트래픽 급증을 쉽게 처리하기 위해 수천 개의 인스턴스로 확장할 수 있습니다.
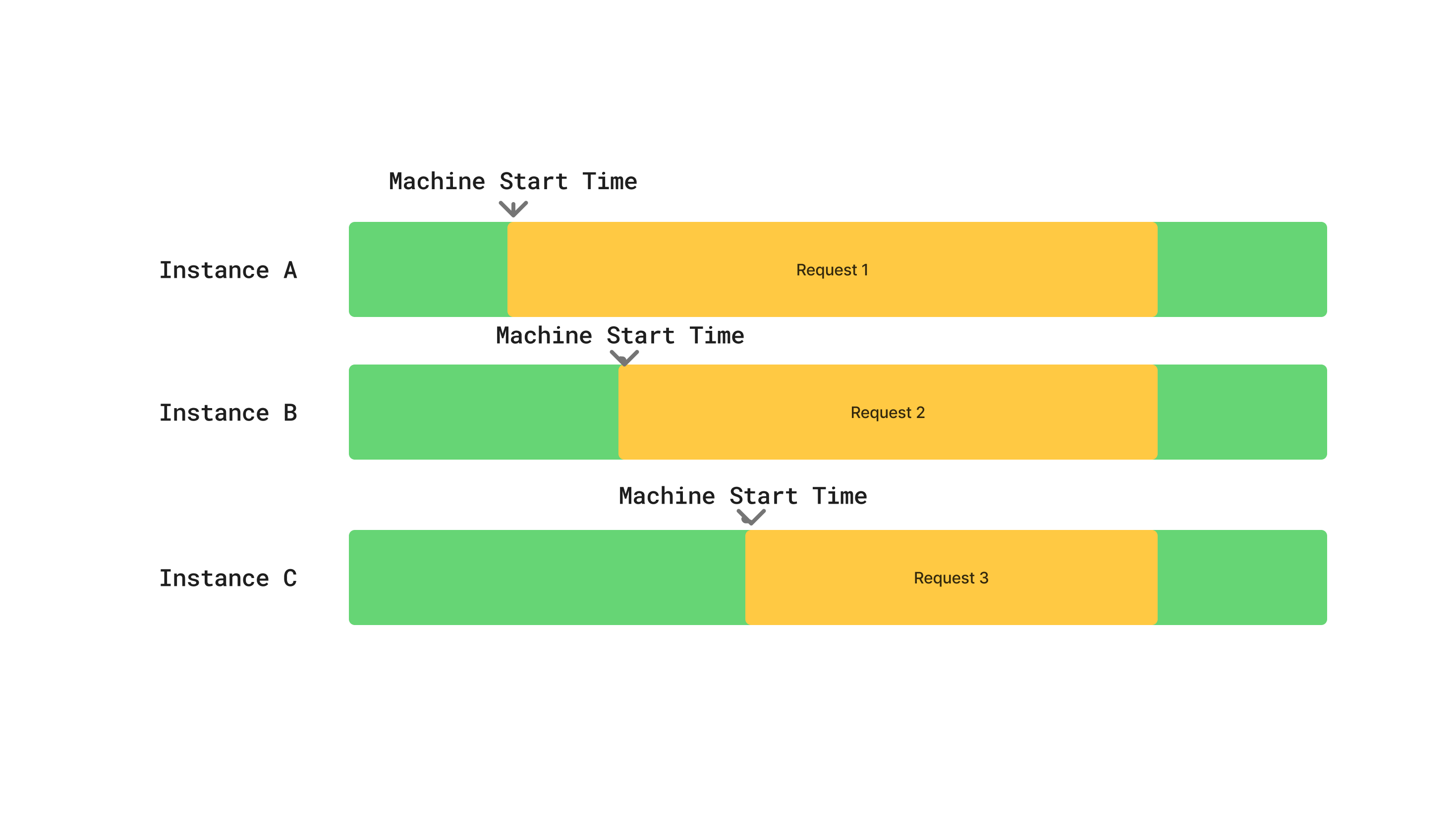
콜드 스타트
서비스에 일정 기간(예: 30분) 동안 트래픽이 없으면 해당 인스턴스가 휴��면 상태가 될 수 있습니다. 새로운 수신 요청은 새 인스턴스를 프로비저닝하기 위해 "콜드 스타트"를 트리거하며, 이로 인해 최대 250ms의 지연 시간이 추가될 수 있습니다. 일관된 트래픽을 가진 서비스는 이러한 현상이 드뭅니다.

서버리스 장점 및 제한 사항
주요 장점
| 장점 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 비용 효율성 | 유휴 리소스에 대한 요금을 없애므로 변동성이 크거나 예측할 수 없는 트래픽 패턴을 가진 애플리케이션에 이상적입니다. |
| 자동 확장 | 플랫폼은 트래픽 볼륨에 따라 인스턴스 수를 자동으로 확장하거나 축소합니다. 트래픽 급증을 쉽게 처리하기 위해 수천 개의 인스턴스로 확장할 수 있습니다. |
고려해야 할 제한 사항
| 제한 사항 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| HTTP 단기 요청만 가능 | 서�버리스 모델은 단기 HTTP 요청에 최적화되어 있습니다. WebSockets, 롱 폴링 또는 백그라운드 작업과 같은 장기 실행 연결에는 적합하지 않습니다. |
| 임시 파일 시스템 | /tmp 디렉터리만 쓰기 가능합니다. 파일 시스템의 다른 모든 경로는 읽기 전용입니다. |
| 요청 시간 초과 | 단일 요청에 대한 최대 실행 시간은 15분입니다. |
| CPU 일시 중단 | 유휴 기간 동안 인스턴스의 CPU가 일시 중단됩니다. 즉, 수신 요청이 없을 때는 백그라운드 작업을 실행할 수 없습니다. |
영구 모드(시간별 요금)
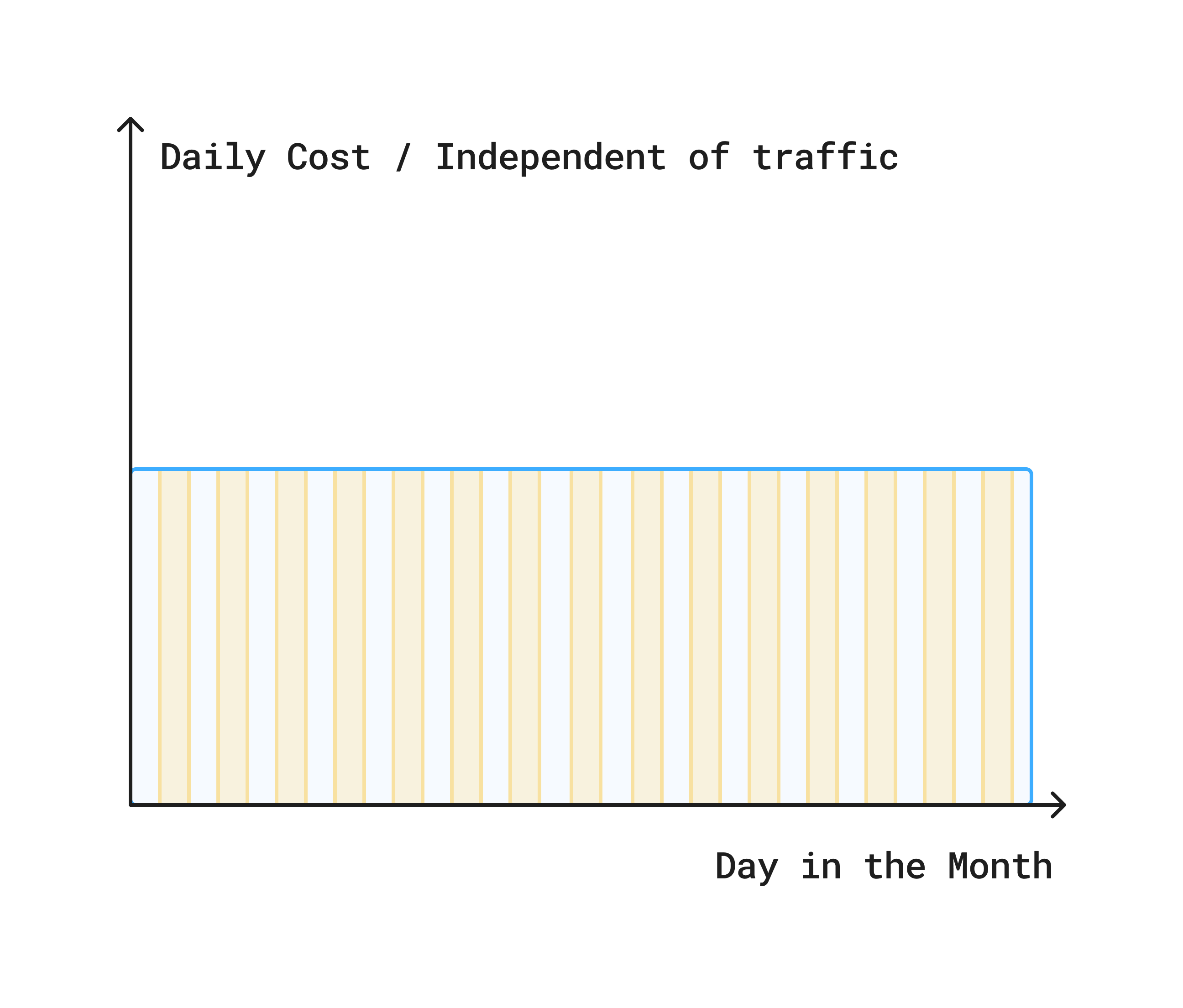
영구 모드는 로컬 머신 또는 기존 클라우드 서버와 마찬가지로 전용의 지속적으로 실행되는 인스턴스를 제공합니다.
인바운드 요청 볼륨에 관계없이 항상 활성 상태를 유지하고 트래픽을 처리할 준비가 되어 있습니다. 이 모드는 시간당 또는 월별과 같은 고정된 시간 간격을 기준으로 요금이 청구됩니다.
주요 장점:
| 기능 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 단위 시간당 저렴 | 고정 요금 모델은 안정적인 워크로드를 가진 애플리케이션에 더 비용 효율적일 수 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 Leapcell 가격 책정을 참조하세요. |
| 콜드 스타트 없음 | 인스턴스가 항상 활성 상태이므로 모든 요청에 대해 가능한 최저 대기 시간을 보장합니다. |
| 파일 시스템 | /tmp 디렉터리 이외의 쓰기 가능한 파일 시스템을 제공하여 로컬 파일 I/O, 캐싱 및 상태 관리를 지원합니다. |
| 장기 실행 작업 | WebSockets과 같이 백그라운드 작업, 데이터 처리 또는 지속적인 연결 유지와 같이 일시 중단 없이 장기간 실행해야 하는 프로세스에 이상적입니다. |
내 사용 사례에 서버리스 또는 영구 서버가 적합할까요?
대부분의 사용 사례에서는 뛰어난 유연성과 비용 효율성으로 인해 서버리스 모드로 시작하는 것이 좋습니다.
서버리스를 사용해야 하는 경우
| 서버리스를 사용해야 하는 경우 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 모든 상태 비저장 HTTP 또는 웹 서비스 | 애플리케이션 상태는 서비스 자체가 아닌 객체 스토리지 또는 데이터베이스에 저장해야 합니다. |
| 예측할 수 없는 초기 단계 트래픽이 있는 서비스 | 초기 단계에서 트래픽이 낮거나 불확실한 경우 서버리스 모델이 가장 비용 효율적인 선택입니다. |
영구 서버를 사용해야 하는 경우
영구 모드는 다음과 같��은 시나리오에서 뛰어난 선택입니다.
| 영구 서버를 사용해야 하는 경우 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 높고 지속적인 트래픽 | 서비스가 지속적으로 높은 트래픽을 처리하는 경우 영구 인스턴스의 시간당 비용이 빈번한 서버리스 호출의 누적 비용보다 낮을 수 있습니다. |
| 장기 실행 백그라운드 작업 | 비디오 인코딩, 복잡한 데이터 분석 또는 머신 러닝 모델 학습과 같이 15분 제한을 초과하는 작업의 경우. |
| 로컬 파일 시스템에 대한 종속성 | 애플리케이션에 캐싱 또는 상태 관리와 같이 /tmp를 초과하는 영구 로컬 스토리지가 필요한 경우. |
| 매우 낮은 대기 시간 요구 사항 | 가끔 발생하는 콜드 스타트로 인한 최소한의 대기 시간조차 허용할 수 없는 애플리케이션에 이상적입니다. |
| WebSockets 또는 장기 연결 | 서비스에 WebSockets 또는 기타 장기 연결이 필요한 경우 영구 서버를 사용해야 합니다. |