How Leapcell Works
If the solution below does not resolve your issue, feel free to join our Leapcell Discord community for further assistance.
What is Leapcell?
Leapcell is an application-oriented PaaS platform designed to reduce deployment costs and simplify the software development lifecycle.
Compared to other PaaS products, Leapcell encourages users to deploy all of their code online, enabling continuous optimization and iteration through traffic analysis and CI/CD pipelines.
Our goal is to help you maximize the value of your ideas.
What is a Service (or Project) ?
A Service (or Project) in Leapcell is an application you deploy, run, and manage on our platform.
Leapcell supports applications written in Node.js, Python, Go, and Rust.
We recommend following the principles of The Twelve-Factor App. If you haven’t read it yet, we highly recommend it as a best practice for modern application development.
Your application typically consists of:
- Source code (written in one of the supported languages, possibly using a framework)
- A dependency description file (e.g.,
requirements.txt,package.json) that specifies any additional libraries required to build and run your application
You only need to provide us with these configurations, and we will handle the entire deployment process for you:
- Build Command: A bash command (or a bash script, multi-line commands are supported) that will be executed to build your application. This typically includes commands to install dependencies, such as
pip install -r requirements.txtornpm install. - Start Command: The command used to start your application, for example
gunicorn -b :$PORT app:appornode server.js. - Port: The port your application will listen on for incoming requests. Leapcell Gateway will route incoming traffic to this port.
Additional Configuration:
- Root Directory: The root directory of your application, where the source code and configuration files are located.
What is a Deployment?
Leapcell uses containers as the standard for deployment. The process is as follows:
-
Source Retrieval
- Clone your source code from the configured Git repository (commonly GitHub) and branch.
-
Build Command Execution
- Run your build command defined in project settings.
- Example:
- Python:
pip install -r requirements.txt - Node.js:
npm install
- Python:
-
Image Build
- Send your code to Leapcell’s sandbox environment.
- Build a Docker image using
docker build.
-
Frontend Optimization (Conditional)
- If your project matches Leapcell’s frontend deployment optimization:
- We will extract the static files from your build.
- Upload them automatically to your workspace’s default CDN for high-performance delivery.
- If your project matches Leapcell’s frontend deployment optimization:
What is Service Lifecycle
Service Startup
The diagram below illustrates the full process of how your service starts inside a Leapcell Linux VM.
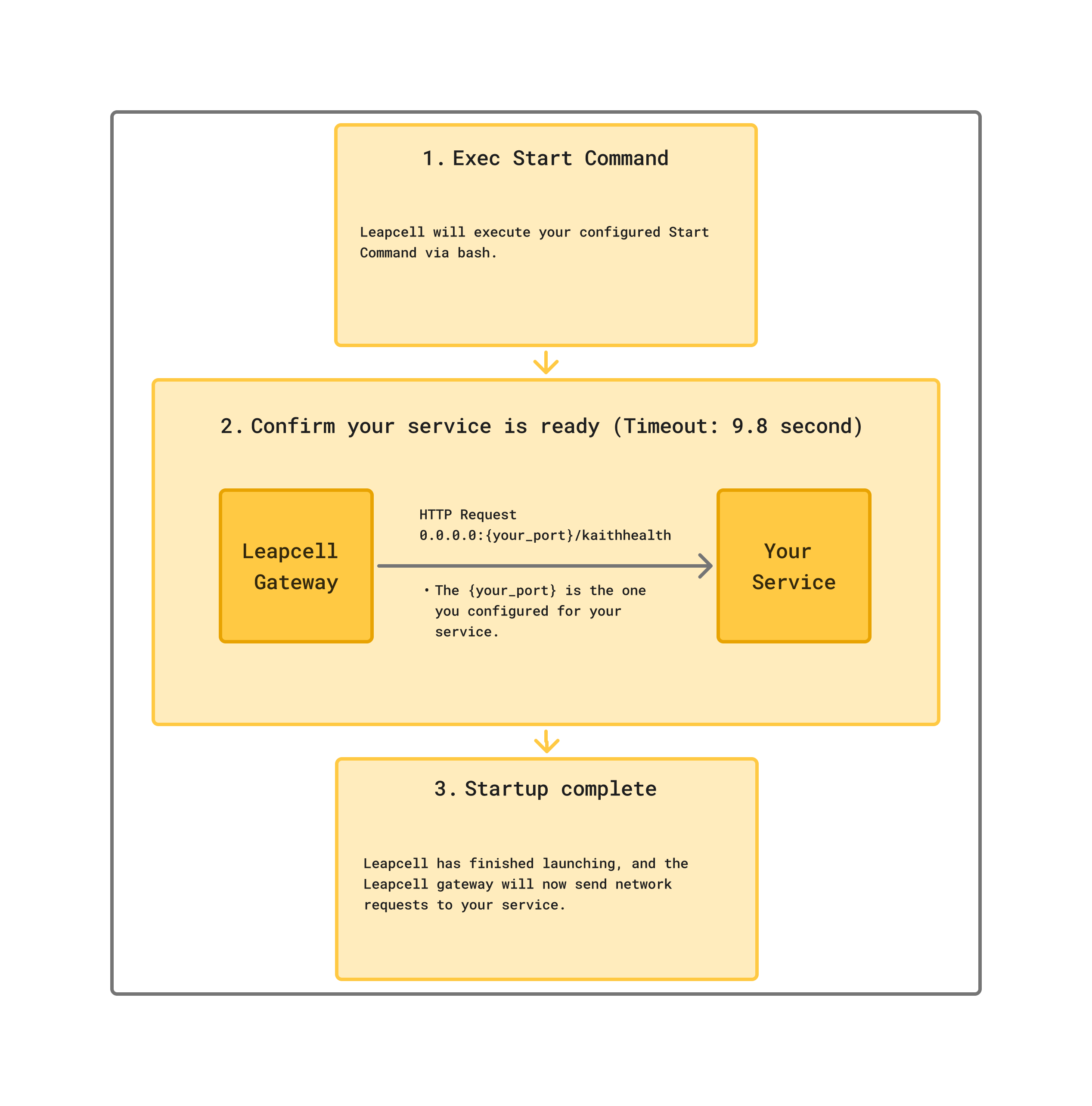
- We execute your configured start command via Bash.
- If your command fails, please check whether your build command missed any dependencies.
- We continuously poll
0.0.0.0:{your_port}/kaithhealthto verify that your port is listening. - Once startup is complete, we route external traffic to your running service.
How Do I Access My Application Service?
After deployment, we will generate a domain with the suffix leapcell.dev for your application. You can simply click the link to access your service.
My Service Failed — How Do I Debug?
Leapcell provides a modern logging infrastructure. You can click the Logs button in the Service Panel to view real-time logs of your service.
Next Steps
We recommend continuing with the following documentation to dive deeper into deployment strategies, scaling, and optimization on Leapcell.